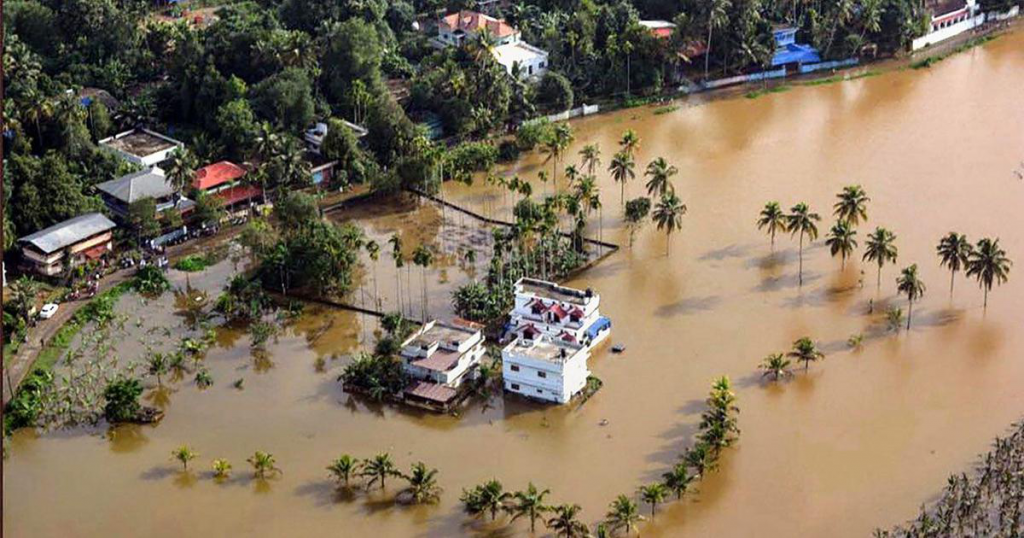

A flood is considered a natural disaster, we cannot stop it from happening at all but we can definitely avoid heavy losses if we plan well. With respect to buildings, taking a few precautions, and encouraging flood-resistant construction techniques can help us mitigate a lot of losses. Read on to know more about some of the reasons for flooding and techniques we must follow to reduce losses.
Basically, flooding is a condition in which land is completely submerged in water which otherwise is normally dry. The low lying area adjacent to a river plain is called flood plain, which is made up of sediments of the river. It is highly fertile. At the time of the flood, water spills to this flood plain causing flooding. These areas are usually thickly populated as the land is very apt for cultivation.
In Kerala, we didn’t see much flooding until three years ago. Prior to that, the biggest flooding event Kerala saw was in the early 1920s, about a century ago, when most of us were not even alive. But now the scenario has completely changed as we experienced back to back floods in the last two consecutive years.
Here are some of the reasons why flooding happens:
- Infiltration or run-off rate will be lesser than the rate of precipitation in a flat or low lying land.
- High water level due to strong storms combines with natural high tide in coastal areas.
- In urban areas, due to improper drainage systems and high precipitation, water can accumulate in the streets and can backflow into building through sewer pipes when rainfall is higher than drainage capacity.
- Rainfall, monsoon, and tropical cyclones lasting for a longer period of time than usual.
- Condition of flood worsens in case of infrastructure failures like dam mismanagement.
6 must-follow flood resistant buildings construction techniques
Although there are limitations to control flood as it is a natural calamity, we can take certain safety and preventive measures to ease the effects.
1. Selection of Construction Site
We should always be careful while selecting a site. The first and most effective technique is to locate the site outside the flood plains. You can accomplish this by checking the flood maps and avoiding buildings within the flood plain. Sometimes, this may not be practical due to the unavailability of land or financial issues. The chances of flooding are more when it is near to the river. Always make sure the site is restored to its natural conditions. That means, design the building according to the contour of the site so that the natural flow of the water is not obstructed.
2. Road and Drainage Levels
We should always consider the level of the site in relation to road. Always maintains the site at a higher level expecting the elevated road after repair and maintenance. So that there is no chance for the backflow of water to the site during heavy monsoons. Similarly, ensure slope of an outlet drainage pipe in such a way that chance of backflow is sealed. The depth of drainage is also critical. This is very helpful for construction where the flooding level is low.
3. Raising The Elevation
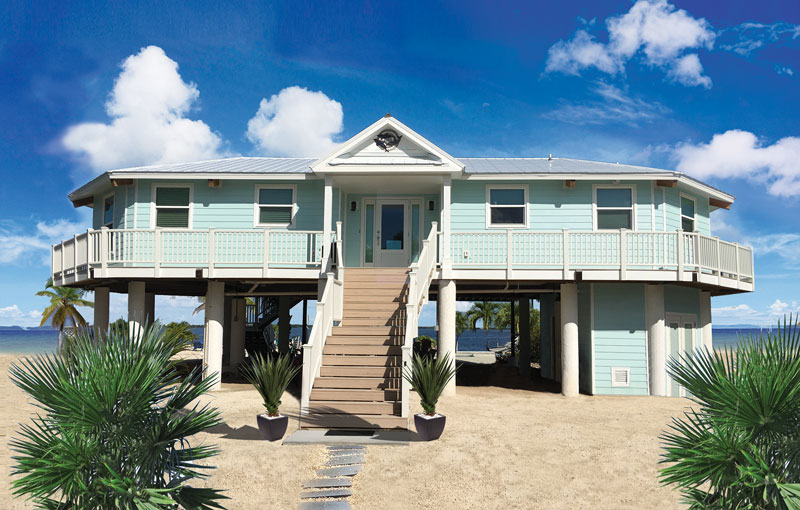

The house can be raised enough on some supports which should be sufficiently strong enough to bear the load of structure and forces acting by flood water and have ample space for the passage of water. You can do this by designing the building so its lowest floor is located at or above the flood level. You can either keep it as vacant or use as car park or storage.
4. Foundation
You need to design and construct the foundation of flood-resistant buildings in such a way that withstands design flood circumstances. It should have adequate capacity to resist floating, collapse, and permanent lateral movement under the critical load combinations. The foundation design of flood-resistant buildings should depend on the geotechnical characteristics of soil and strata beneath the foundation.
5. Wet Flood Proofing
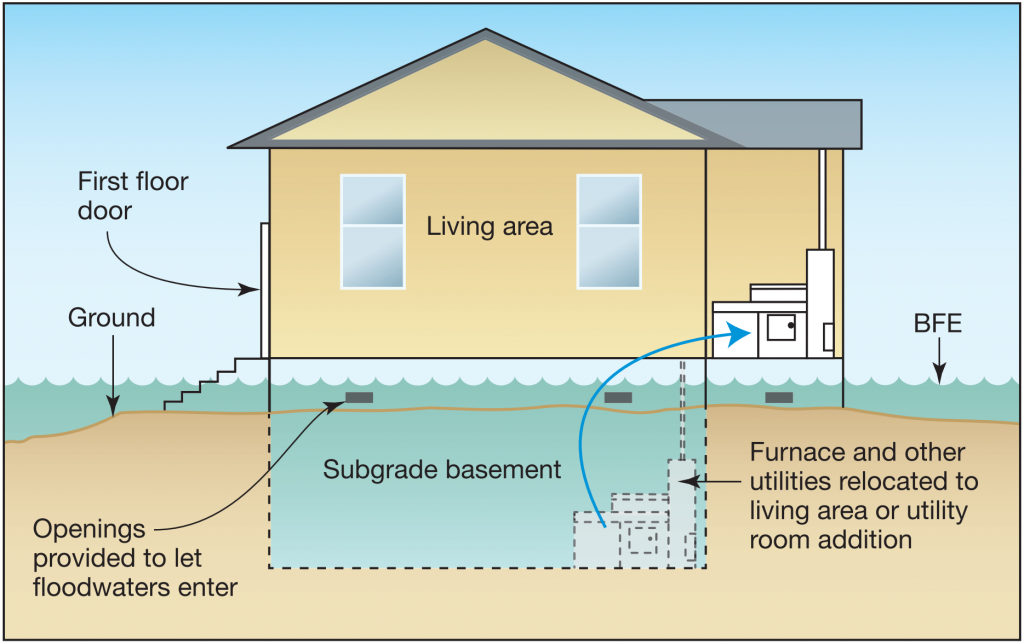
Wet floodproofing involves controlled and safe passage of floodwater through lower levels of the house. The sewers and water system should be above water level or should be sealed when the water rises above them to avoid health hazards. Keep the inlet points open well before any pile-up of water fills up to avoid pressure at the structure. The use of flood vents, flood damage-resistant building materials, and protecting service equipment by locating them above the anticipated flood elevation are all methods of wet floodproofing.
6. Dry Flood Proofing
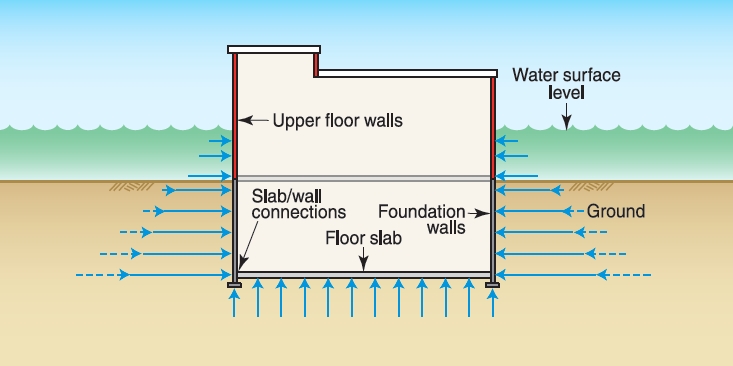
If relocating or elevating the building isn’t feasible, then wet or dry floodproofing can reduce the risk of flood damage. Dry floodproofing techniques essentially make the building watertight by adding sealants to the walls, shields to the openings, and secondary drainage and pumps to remove the water that seeps inside the building. This technique is good for concrete or masonry construction with low levels of flooding. But it does require significant levels of maintenance.
Overall, we can minimize the impacts of these damages by implementing siting, design, construction, and maintenance practices that are suitable to floodplain areas.
What do you think? Share your thoughts below.