Manufacturing, whether its your car or smartphone, is a very evolved process with more than a couple of 100 years worth of learnings going in to it. Well, probably more so from the time Henry Ford introduced integrated moving assembly line for production of famous Model T cars as early as 1913!
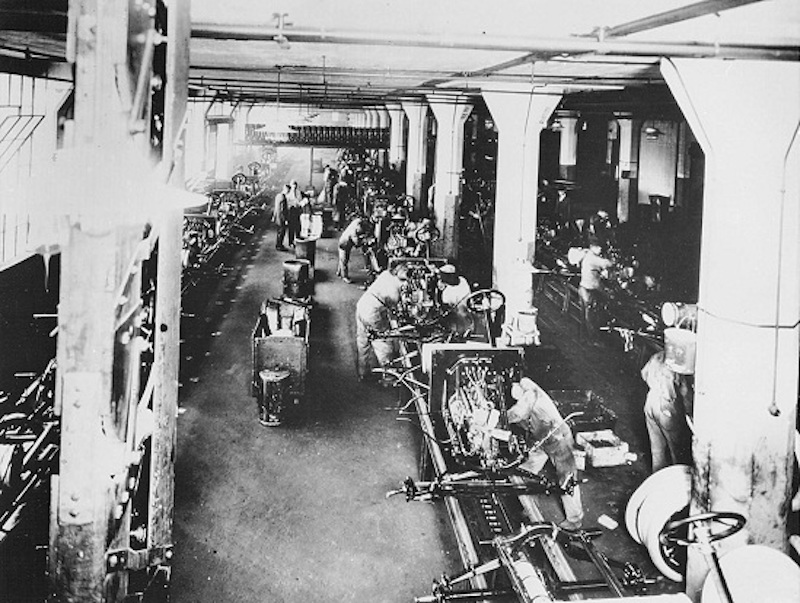

From Ford to Toyota, the extent of learning and improvement which went in to manufacturing process, particularly assembly line, has led to significant savings due to increased efficiency of production. As a result, products are now accessible at much more affordable costs. Greater the efficiency, lower the wastages, ergo lower costs – well, if the manufacturer deems to pass on the earnings to you!
If you think about it, construction industry is even older than the manufacturing industry. Simply because it caters to one among our most basic needs of food, clothing and a house! So from the time civilization started, we humans have engaged in construction site. Very large cities discovered of erstwhile civilizations – whether its Indus Valley, Mesopotamia or ancient Egyptian – proves this point. There have been cities as old as 5000BC or more in Aleppo, Athens or Jericho.

Why then did we fail to achieve the same efficiency in construction like in manufacturing? Construction is a much more expensive and complex effort. So why are there no examples like a Ford or Toyota in construction?
Why should we invest in improving efficiency in construction?
Lets take the Indian scenario. Lets look at 2 strata of construction – affordable housing and middle class housing. An average standalone affordable housing project costs anywhere between 6-10 lakh rupees. An average standalone middle class housing project costs between 30lakh to 60lakh rupees. So a 10% saving in efficiency of production keeps anywhere between 60000 to 3lakh rupees in your pockets, looking at the lower end of spend.
Moreover, the amount saved in building materials will help us build in a more sustainable manner to the eco-system. So we owe it to the future of our planet to be responsible, and we owe it to ourselves to invest in improving construction site efficiency and reducing wastage in the most complex and expensive product – building projects.
Now that we know there is a lot to gain by focusing on improving efficiency in construction site, let’s look at how we can take the learnings from manufacturing to construction. One major challenge is that construction doesn’t happen inside a factory. We need to look at construction as in-situ manufacturing. Broadly, there are 4 important things we need to review before focusing on the finer details of improving production efficiency:
1. Planning
Manufacturing process is meticulously planned with detailed 3D modelling of each component, irrespective of the size. One of the major reasons construction process fail to get consistent construction efficiency is lack of accurate and detailed planning. Inefficiency becomes manifold, as the number of components – materials, labor and machinery – needed to complete a project is much higher in construction. So the first thing we need to do is invest time and effort in accurate planning.
Now there are methods to be as close to component modelling in manufacturing. For example, new age technologies like virtual reality can greatly aid in getting the detailing of your project accurate. Virtual reality helps both the planning architect as well the client to walk through and get a near perfect approximation of the space that they are going to build.
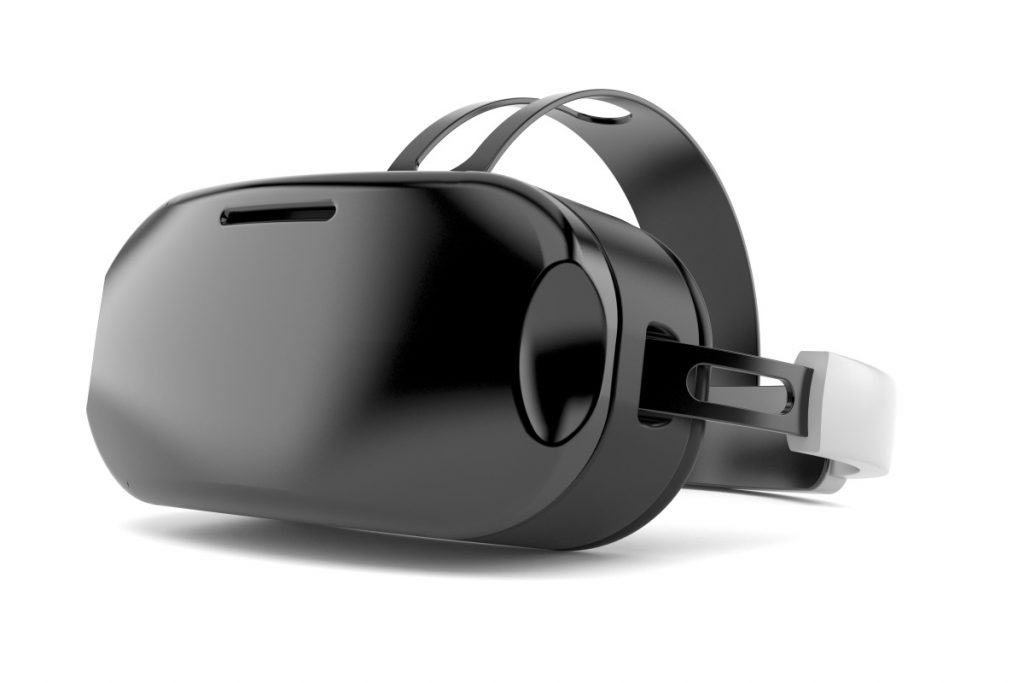

Another useful tool is BIM (Building Information Modelling), where everything can be integrated in planning just like in manufacturing. VR and BIM can be interlinked too, with former offering a more user friendly experience to the details.
Planning doesn’t stop there though. We should know exactly what materials in what quantity needs to go in to each activity/module of construction. We will need to know exact amount of labor manhours that is needed as well as the machinery. Project management usually involves this level of planning. There are players in the market who goes to this level of planning.
2. Standardization
Another important aspect to gather construction site efficiency is to standardize the processes. In construction, unless you are building flats or villa projects, every customer will make their custom choices on the components. This stops construction from achieving economies of scale-like in an assembly line manufacturing process where every component is standard.
It’s probably also not fair to ask every customer to choose the same component, after all, home building is a very emotional process too. The amount invested is also much higher. The next best thing then will be to standardize a set of components needed to complete an activity in the construction process. This will will have elements from design, materials, labor and machinery.
For example, take foundation of building. It requires design, a certain set of materials, labor and machinery. Standardization is done by pre-determining a consistent design style which factors in construct-ability and then assessing the components required to build a single cubic metre of foundation. Various projects can then use these same set of standards. By doing this, entire construction process becomes a combination of standard activities used in differing quantities.
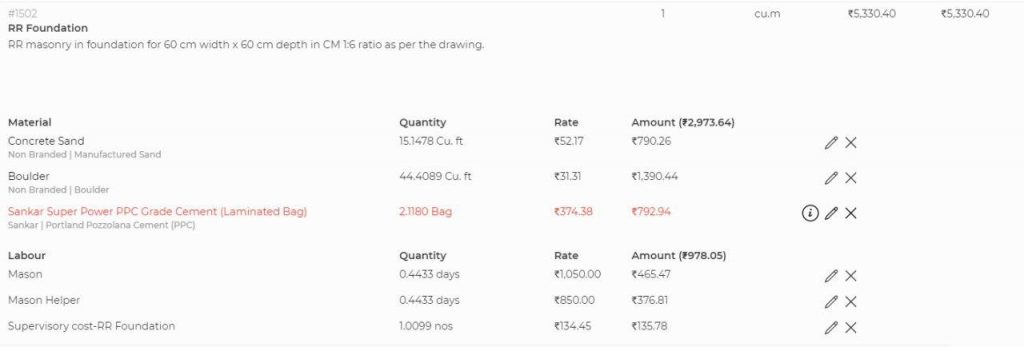
The more standards you have as input, the more predictable is the construction process. Just like manufacturing.
3. Modularization/Pre-Fabrication
Another method to introduce manufacturing efficiency in construction is by implementing modularization or pre-fabricated components. Most commonly used example is ofcourse, modular kitchen. Pre-fabrication helps taking out some of the construction process from the site, to actual factories.

Nowadays, there are companies who do entire construction within factories and then assemble them at site. But since it’s not feasible for standalone projects in India, due to various reasons like infrastructure needed for large machinery movements and relatively cheaper labor available locally, we will focus on component modularization.
Some of the common and easily achievable options are doors, windows, kitchen as discussed above, wardrobes, and furniture. These products are already made in manufacturing facilities, thereby directly bringing in those efficiencies. But the trick lies in coordinating their installation by looking at overall construction as a manufacturing process at site. We just get much larger components made in parallel away from the site, thus speeding up construction, reducing labor and effort needed at site.
4. Construction site coordination using a factory approach
Once we have spent time and effort in ensuring the above 3, the most important factor is coordinating all of these at site, in true factory floor approach. Lets look at how we can use Toyota Production System (TPS) principles at construction sites using technology.
Kaizen (Continuous Improvement)
In the earlier section, we discussed that all activities involved in construction process should compulsarily have standards. Once you have standards, this will act as base data against which you can constantly monitor progress at work sites. Any variance between actual work happening at site and the standards we set are data points that will lead to eventually adjusting the standards. This is what continuous improvement is all about.
Another important factor is having a culture of continuous improvement within the resources who are managing the project. Right resources can ensure necessary steps will be taken at the right time. In a nut shell, just by having right resources and standards prior to construction and a mechanism to collect data from sites on a daily basis to compare to these standards, your construction site becomes Kaizen enabled!
Kanban or E-Kanban for Just-in-Time (JIT) Execution
One of the methods factories use to improve efficiency and reduce wastage is by moving to a pull based system for resources. For example, material reaches work site exactly when it is needed, or labor is scheduled accurately in such a way that there is no idle time. How can we make this possible? Answer lies in implementing Kanban or E-Kanban (Electronic Kanban).
The only way this is possible in a construction is if you make use of technology tools for managing the project. Purchase Order for materials is in one way a Kanban system, but it becomes efficient only if delivery is done just in time. Similarly, there are software that can predict labor requirement accurately based on plan, so that there is no idle time.
Muda Reduction
Muda means waste in Japanese language. According to Toyota system, wastage happens in 7 forms:
- Transportation of unwanted products for a process or activity
- Inventory
- Motion of people or resources that is unwarranted
- Waiting for production
- Overproduction
- Over processing due to poor tools or design
- Defects
All construction sites have most of these types of waste. But with careful planning and right kinds of technology, we can greatly reduce all of them. The idea is to adopt latest software that helps in project planning, including project management software like BuildNext PRO, Virtual Reality and BIM.
Lean Construction Practices
Lean construction adopts best practices from lean manufacturing process – a culmination of all the above mentioned steps. Emphasis is on reduction of wastages and making processes efficient right from designing phase through handover. Sometimes, Six Sigma tools can easily help you execute what all these approaches are campaigning for.
Six Sigma says to have a framework similar to DMAIC – Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control. This is exactly what we covered in the above sections. We need to set standards, implement process to capture data from sites to measure, analyze variances, improve standards based on analysis and implement control mechanisms including active monitoring.
As we can see, manufacturing has a clearly defined approach for efficiency improvement available. We can easily adopt these in to construction process with the right set of tools. This will help us save money, time and ultimately build in a more sustainable way for the future.
Do you think every construction site should adopt a factory approach?
Good one! Well explained. Worth reading .
Fascinating read, drives the case home.